We Can Replace Your Existing vortex Grit system
to Perform Like New regardless of original manufacturer
The headworks of a wastewater treatment plant can be degraded by biogenic corrosion. Grit removal equipment is critical to the operation of the wastewater treatment process. Sulfuric acid is formed biologically and can corrode concrete and steel structures and equipment. Grit removal equipment can be affected by this process. Motors, gearboxes, bearings, valves and fittings can have accelerated wear and tear. Materials such as cast iron or ductile iron can be especially prone to accelerated corrosion. Hydro-Dyne Engineering can replace equipment within a vortex grit removal system regardless the manufacturer to establish original performance.
Hydro-Dyne Engineering is an original equipment manufacturer of a full range of vortex grit removal equipment. Parts and service can be supplied to replace aged or non-performing equipment. A service visit to provide system diagnostics is available if needed.
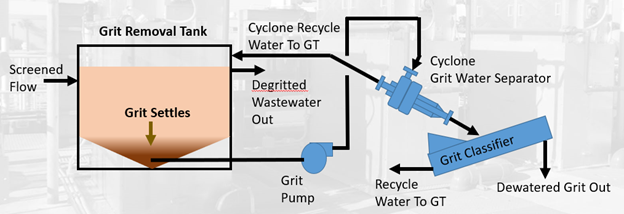
Grit that settles in the bottom of a grit settling tank is typically a slurry consisting of 98% water and 2% or less solids made up of fine sand, shell, bone and other fine solids larger than 300 microns in size. Grit slurry is then pumped to be further dewatered by a cyclonic device followed by additional settling. The schematic below provides a diagram of the grit slurry removal and dewatering process. Note the grit pump can be configured in two ways, either on top of the tank to provide a suction lift or as shown below with a flooded suction supply from the tank bottom. The diagram is also simplified and does not show a fluidizing line used to keep grit slurry in suspension for transport to the dewatering process.
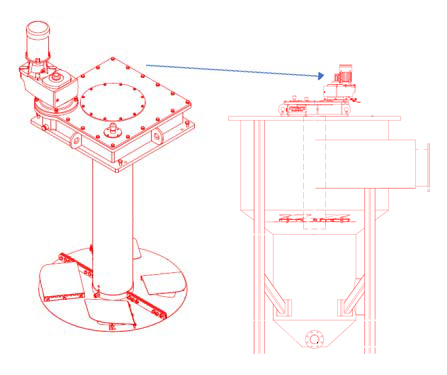
A typical impeller assembly is shown for a concrete grit tank with a sloped floor design. Common replacement items include the motor and/or gearbox located at the top of the assembly. The impeller used in this design is typically submerged and can be replaced as well. An impeller assembly design for a sloped floor grit tank is included in the image shown. It is important to note that this assembly is specific for a flooded suction grit slurry pump. A different impeller design is utilized for a grit slurry removal pump mounted on top of the tank.
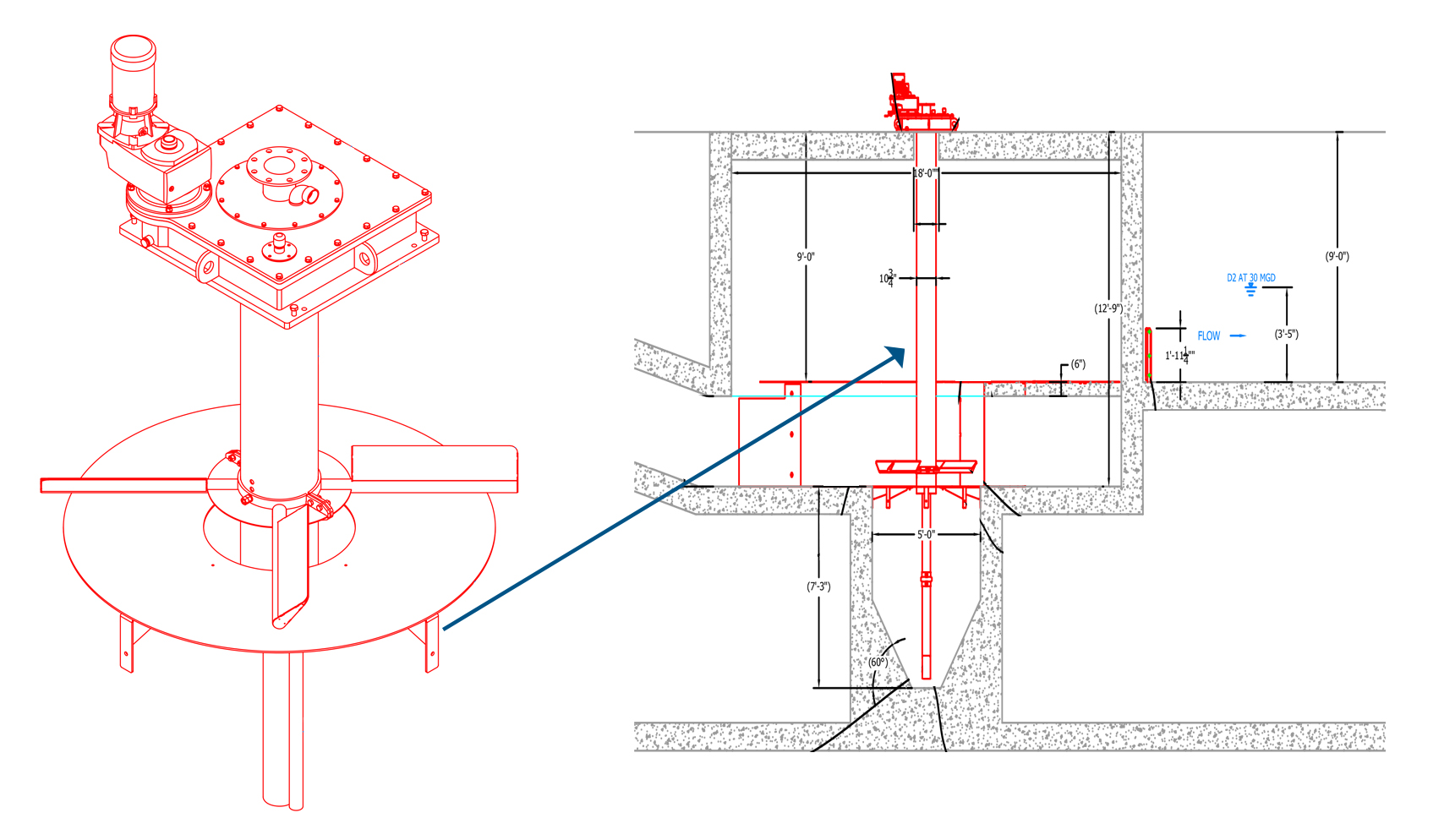
A typical propeller assembly is shown for a concrete grit tank with a flat floor design. Common replacement items include the motor and/or gearbox located at the top of the assembly. The propeller used in this design is typically submerged and can be replaced as well.
A propeller assembly design for a sloped floor grit tank is included in the image shown. It is important to note that this assembly is specific for a top mounted grit slurry pump. Note the flange on the top of the assembly near the motor used to connect to a grit slurry pump influent. A different propeller design is utilized for a grit slurry removal pump mounted on at the bottom of the grit tank.
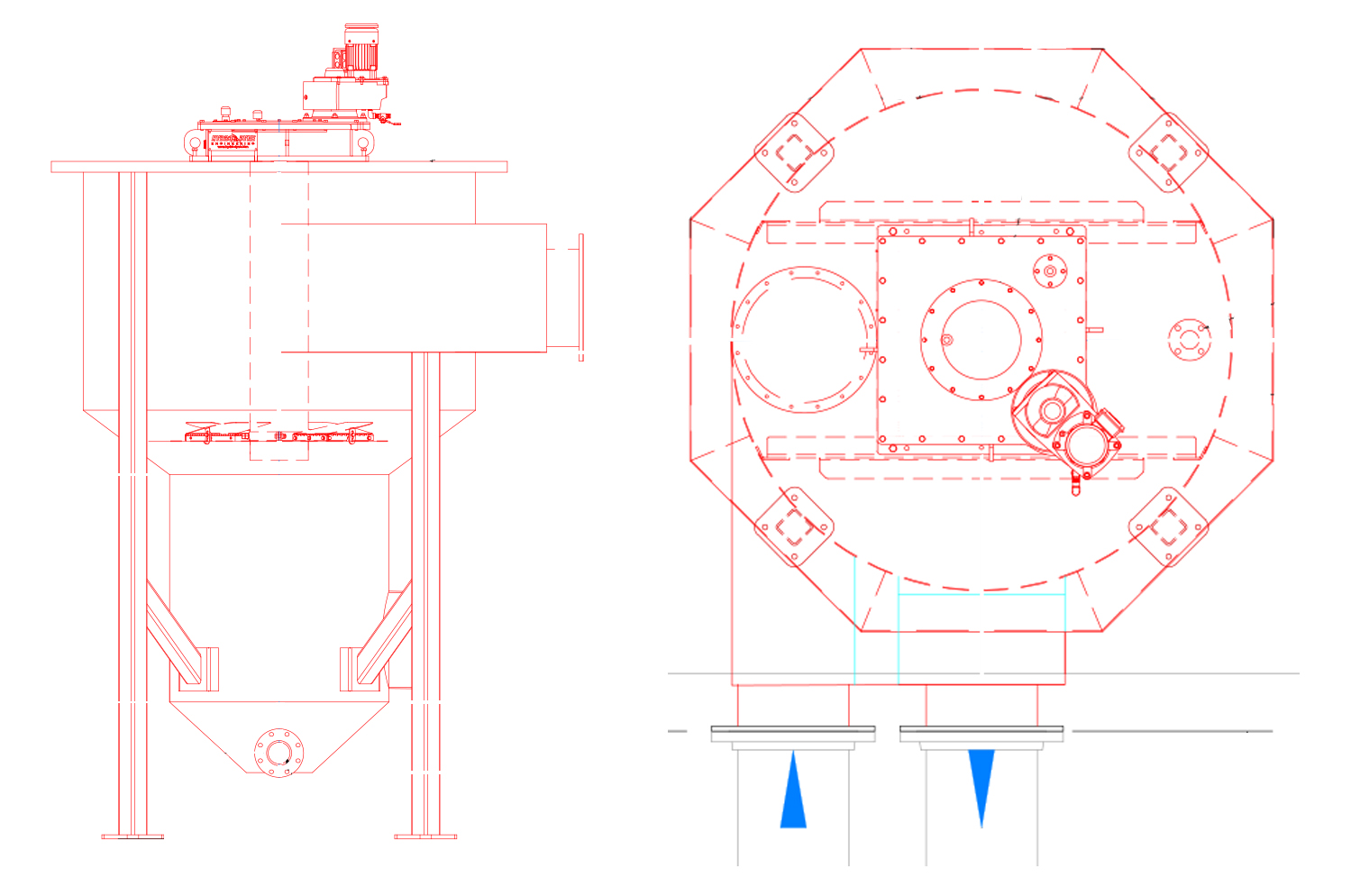
Hydro-Dyne can fabricate tanks from stainless steel. These are typically used for smaller grit removal tanks. These tanks with systems below a flowrate threshold of 5 MGD. A small 6’ diameter sloped floor grit removal tank is shown below. The overall tank height on this design is 10’ tall. Stainless steel can have pitting or crevasse corrosion if the tank was not initially passivated correctly. Hydro-Dyne can provide a replacement tank if corrosion is advanced.
A pump is commonly used to remove grit slurry from the grit settling tank. The pump is specialized to handle highly abrasive slurry. The grit slurry pump can have a flooded suction as shown in the schematic above or be mounted on the top of the grit settling tank to draw grit from the tank bottom to the pump impeller. A centrifugal single stage pump with casing and recessed impeller design is used for this service as grit slurry is abrasive to rotating equipment. The recessed impeller has the capability to transport solids with low propensity to bind rotating parts.
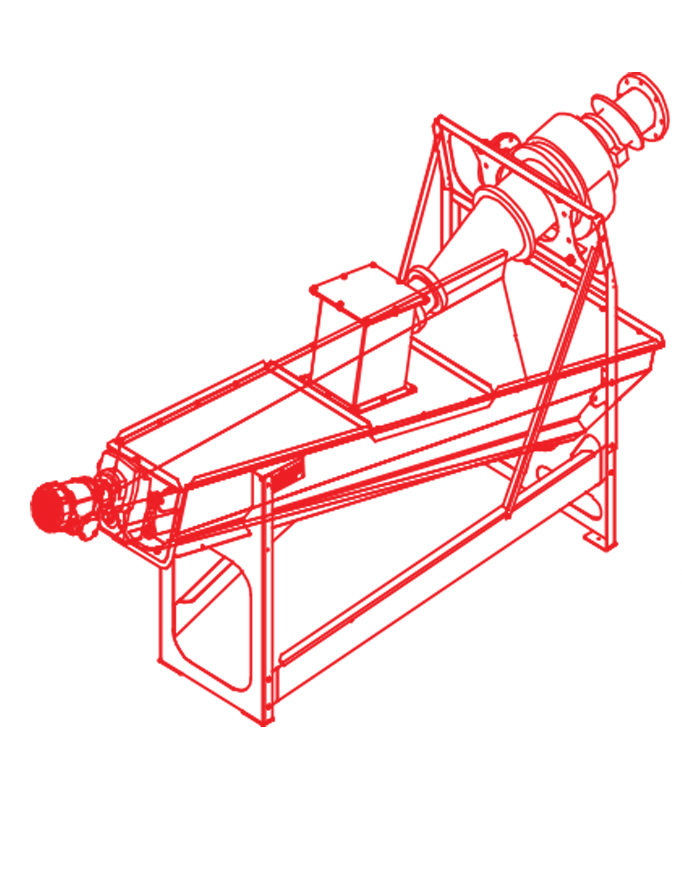
The grit classifier is a key component used to dewater grit slurry from a grit removal tank. A cyclone is commonly used to remove 90% of the water from the grit slurry before it enters the grit classifier. A grit classifier is composed of a small settling tank for grit where an auger transports grit out of the settling zone to a final disposal vessel that is either a dumpster or bag. Grit slurry is extremely abrasive and can wear down any rotating equipment in contact. A schematic below shows a 3D view of a grit classifier with cyclone.
Get customer input to understand recognized equipment needs
Require and recommend a scope of work for appropriate replacement equipment
Replace agreed to equipment
Re-installation Support to Ensure Achieved Results (Optional)
4750 118th Avenue North Clearwater, Florida 33762 USA Phone: +1 (813) 818-0777 Fax: (813) 818-0770
Copyright ©2025 Hydro-Dyne Engineering. All Rights Reserved. | Privacy Policy | Terms of Use